Micro-Che®
Timing:
SoilNutrient Type:
MicronutrientFormulation:
Liquid
Why a Soil Micronutrient?
The word Micro can leave an impression that these nutrients are not as important to maximize crop production. However, even though the amount required by the crop is small relative to a macronutrient (Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium) the implications of limiting one or more of these essential nutrients can have a dramatic impact on the yield of the crop.
Over the previous number of decades stewardship to micronutrient management has not been a top priority giving rise that our soils being depleted with nutrient removal exceeding application rates. However, over the last decade there has been a significant increase in micronutrient management as we need to drive the genetic yield potential of the crop.
One of the challenges is most of the micronutrients (Zinc, Manganese, Copper and Iron) (with the exception being Boron) have limited mobility in the soil meaning deficiencies can show up immediately in the young seedlings.
To ensure the plant does not ever become micronutrient deficiency it is critical to do a soil application using the proper form and placement to optimize nutrient uptake and efficiency by the plant.
The 8 key micronutrients include Zinc, Boron, Manganese, Copper, Iron, Chloride, Molybdenum, and Nickel.
There are a number of benefits of using a soil micronutrient that include (but not limited to);
- Optimize multiple enzymatic processes to maximize photosynthesis.
- Maximize rooting by the crop.
- Ensure proper cell wall and membrane formation in both the roots and leaves of the plant.
- Compliment N, P, K and S nutrition to keep all essential nutrients in balance.
- Important for abiotic stress tolerance.
- Maintain optimum plant health to help the young plants ward off invasion by pathogen and insects (biotic stress).
- In most situations, the micronutrient can be blended with a soil macronutrient program.
To confirm if a micronutrient application is required, it is recommended to do a complete soil analysis for each field. Be sure to include the crop being grown when performing the soil sample as each crop is unique in their micronutrient requirements.
Related Articles
Why Micro-Che?
To Prevent Micronutrient Deficiencies - Add Micro-Che to Your Soil
- Chelation protects the nutrient from being tied up in the soil and allows it to be readily available to the plant.
- Improved nutrient use efficiency.
- Plant available and seedling safe.
- Compatible with Blocker, Convey, UAN, 10-34-0, 3-10-10 and ATS.
Proven Agronomic Performance
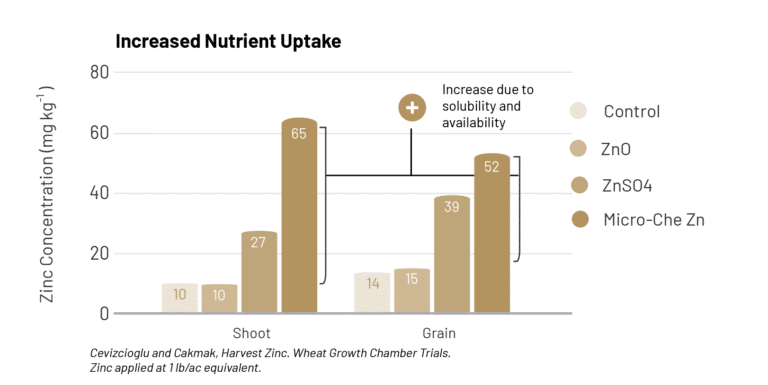
By improving solubility and availability of micronutrients, Micro-Che increased wheat shoot zinc concentration by an average of 65%.
Due to improved solubility of micronutrients, Micro-Che increased grain zinc concentration by an average of 37% in wheat.
See the Difference
Technical Info
| PRODUCT | ANALYSIS | RATE | TIMING | FORM | PRODUCT SIZE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-0-0-9.0Zn + 40.6% EDTA | 0.5-1.0 qt/ac | Soil | Liquid | Case (2x2.5 gallon, 250 gallon) | |
| 7-0-0-7.5Cu + 34.6% EDTA | 0.5-1.0 qt/ac | Soil | Liquid | Case (2x2.5 gallon, 250 gallon) | |
| 3-0-0-6.0Mn + 35% EDTA | 0.5-1.0 qt/ac | Soil | Liquid | Case (2x2.5 gallon, 250 gallon) | |
| 4-0-0-10.0B | 1.0-2.0** qt/ac | Soil | Liquid | Case (2x2.5 gallon, 250 gallon) |
Product Recommendations:
- Apply Micro-Che with your liquid in-furrow or banded fertilizers.
- Please conduct a soil sample to determine if your soil will be responsive to a liquid micronutrient application and assist in determining the optimum application rate.
- *Micro-Che Zn, Micro-Che Mn, Micro-Che B are compatible with ATS. Please note, Micro-Che Cu is not compatible with ATS.


