Pulse
and how to use plant nutrition and biostimulants to maximize the crops genetic potential.
What are the nutritional requirements of a pulse crop?
Watch the video to learn about what nutrients are required by a pulse crop and the best times to apply them.
Essential nutrition for pulse crops
Essential nutrition for pulse crops can be divided into four key stages. Preventing a nutrient deficiency at each of these stages is crucial for preserving the genetic potential of the crop to maximize yield potential yield potential. Use the tabs below to learn about the key nutrients required for each stage:
(Herbicide Timing)
(Fungicide Timing)

Seeds are naturally nutritionally imbalanced – adding a seed nutrient dressing can help the seedling get off to a strong start.
- Add an Inoculant to the seed to drive Nitrogen fixation.
- Pulse crop seeds are naturally nutritionally imbalanced – adding a seed nutrient dressing can help the seedling get off to a strong start. However, caution must be taken to ensure nutrient like Zinc are not added as it can harm the inoculant you apply to your pea seed.
- Nutrients such as molybdenum formulated with biostimulants (Transit-S and Cellburst) can help drive rooting and enhance early seedling vigour, without having negative effects on the inoculant.
- The other key goal with adding biostimulants to the seed is to address and help overcome early season stresses, such as cold soils.

To address the needs of the seedlings (and limitations within the seed) it is vital to ensure the soil has the key nutrients properly placed (either seed placed or banded close to the seed) to drive rooting, photosynthesis and early season vigor.
- Zinc – auxin production to drive rooting
- Manganese – photosynthesis (responsible for splitting the H2O molecule)
- Boron – cell membrane integrity for strong, healthy roots
- Biostimulants (Synergro M2) – drive rooting and improved nutrient use efficiency
- Phosphorus* – energy production and photosynthesis
Seed placed Phosphorus can injure a pulse crop and should NOT be applied in the seed row. If you are applying phosphorus, apply as a side or deep band.
(Herbicide Timing)
 During the vegetative growth stage, the crop is ramping up nutrient demand and energy production while still having a limited root system to acquire nutrients from the soil. The 3-5 leaf stage (3rd to 5th node) is the ideal timing to combine these critical nutrients with a herbicide application to meet the increased nutritional demand of the crop and optimizing each pass across the field:
During the vegetative growth stage, the crop is ramping up nutrient demand and energy production while still having a limited root system to acquire nutrients from the soil. The 3-5 leaf stage (3rd to 5th node) is the ideal timing to combine these critical nutrients with a herbicide application to meet the increased nutritional demand of the crop and optimizing each pass across the field:
- Phosphorus – energy production and photosynthesis
- Potassium & Magnesium – critical for carbohydrate movement
- Calcium – cell wall strength and optimizing nitrogen metabolism
- Zinc – root and shoot differentiation and moisture acquisition
- Manganese – optimize enzyme production and carbohydrate metabolism
- Boron – membrane integrity for strong, healthy roots
- Molybdenum – essential for the process of symbiotic Nitrogen fixation by Rhizobia bacteria in legume crops
- Biostimulants (Transit-S and Cellburst) – abiotic stress management, root growth, & improving nutrient uptake and efficiency
(Fungicide Timing)

At flowering, there is a massive nutrient demand on the crop. This is also a time where nutrient acquisition by the soil can be challenged.
At this stage, we need to think about nutrient key nutrients essential for pollination, seed set an grain filling:
- Potassium – water relations, carbohydrate movement from source to sink
- Boron – Essential for the elongation of pollen tubes
- Molybdenum – essential for the process of symbiotic Nitrogen fixation by Rhizobia bacteria in legume crops
- Manganese – Photosynthesis (responsible for splitting the H2O molecule)
- Zinc – auxin production for pollen tube elongation
- Biostimulants (Cellburst) – nutrient uptake and pollen tube elongation
How much nutrition does your crop need?
Use our crop uptake and removal calculator to determine how much of each nutrient is required for your targeted yield.
System of Chemtrition
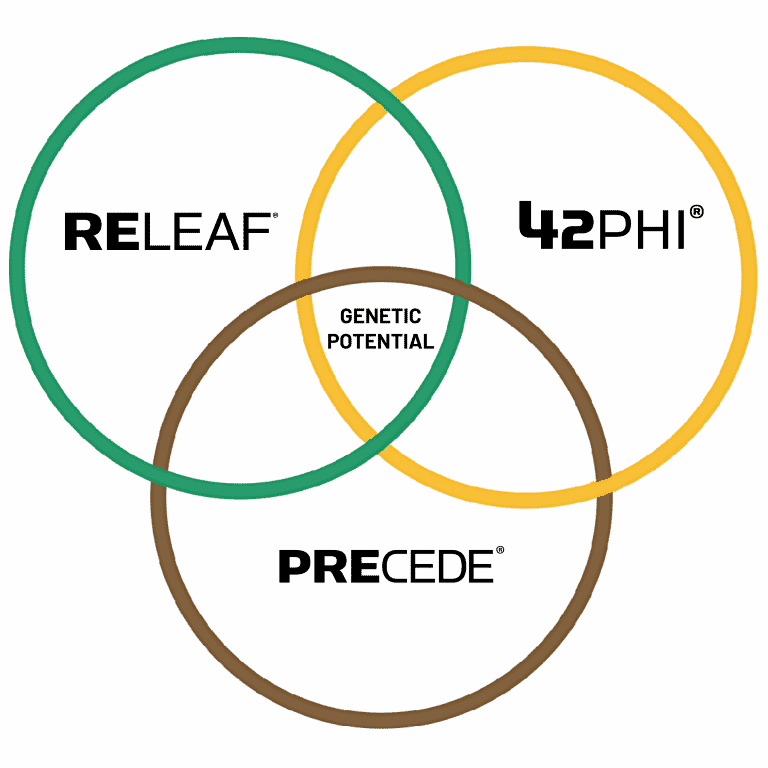
Developed in the lab and perfected in the field, the Chemtrition three-stage system works in tandem with your seed treatment, herbicide, and fungicide plan to deliver essential nutrients throughout the plant’s life cycle. Release the genetic potential of your crop through a proactive, balanced nutrient plan and get the most out of every acre.
Chemtrition = AgChem + Nutrition
PreCede
+ Seed Protectant
Rate: 1.0 L/MT Timing: Seed

- Drive root development, nodulation and maximize nitrogen fixation with the addition of key nutrients and biostimulants.
- Rhizobium friendly formulation.
- Low dose rate ensures flowability of seed when combined with seed protection product.
ReLeaf
+ Herbicide
Rate: 1.0 L/ac Timing: Foliar

- Promote stalk strength and standability with calcium.
- Improve pollination and pollen tube development with calcium.
- Optimum levels of magnesium are essential for synthesis and the transport and storage of important plant substances such as carbohydrates and proteins.
- Drive nutrient uptake and efficiency by the plant with key biostimulants
42PHI
+ Fungicide
Rate: 0.5-1.0 L/ac Timing: Foliar

- Increase nutrient uptake and plant health with the synergy of the fungicide with the optimum load of phosphorus.
- Aids water management and nodule formation with potassium.
- Improves pollen viability and pollination with additional zinc and boron.
Proven Agronomic Performance
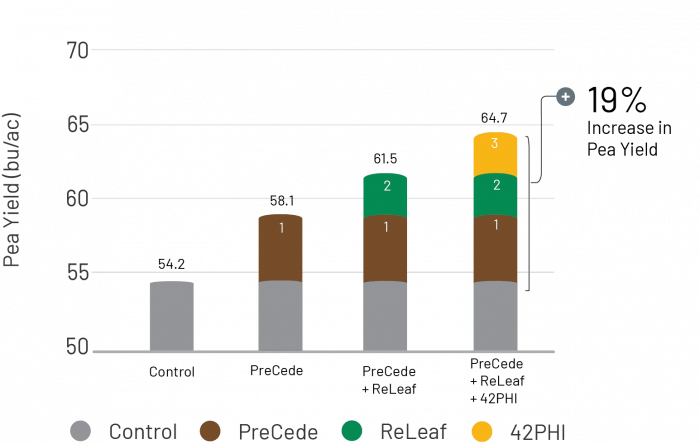
Field trials conducted in North America proved the synergistic effects of the System of Chemtrition in Peas, showing an average yield increase of 19%.
Achieving your genetic potential with pulse
ATP’s pulse nutrition program helps you achieve the genetic potential of your crop – maximizing yield and quality. ATP’s comprehensive product portfolio provides you with a wide range of options to meet all your pulse nutritional requirements.
TIMING
Seed Treatment
Soil
Herbicide
Fungicide
PreCede Rhizo
Transit-S + Cellburst + TE
Ruffin-Tuff Crop Mix ll
6Zn-3Mn-1.5Cu-1.5B-8S
Micro-Che
ReLeaf Pulse
4Ca-1Mg + Transit-S + Cellburst + TE
NRG KB
2-0-15-1.5B + Cellburst
Kinetic Boron
10.0B + Transit-S + Cellburst + TE
42PHI Rhizo
0-36-8-5Zn-3Mn
42PHI K+
0-21-14-0.3Zn + Cellburst
Related Articles

Harnessing the Power of Soil, Tissue, and Seed Tests
Watch the Case Study video showing how one grower proactively used data on his crop – soil test, tissue test and seed test data to
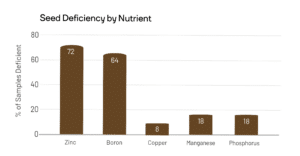
2025 Seed Testing Uncovers Widespread Nutrient Deficiencies
A recent analysis of 489 seed samples has revealed a concerning trend: 91% of the samples showed at least one nutrient deficiency, with nearly half showing

The Importance of Seed Nutrition
The 2025 growing season is just around the corner! Seed nutrient dressings are a powerful, yet relatively economical tool, that will get your crop off