
Cereal
Learn about the essential nutrients required by cereal crops throughout the season and how you can use plant nutrition and biostimulants to maximize the genetic potential of your cereal crop.
What are the nutritional requirements of a cereal crop?
Watch the video to learn about what nutrients are required for a cereal crop and the best times to apply them.
Essential nutrition for cereal crops throughout the growing season
Essential nutrition for cereals can be divided into five key stages. Preventing a nutrient deficiency at each of these stages is crucial for preserving the genetic potential of the crop and maximizing yield potential. Use the arrows below to learn about the key nutrients required for each stage:

Seeds are naturally nutritionally imbalanced – adding a seed nutrient dressing with the following nutrients can help the seedling get off to a strong start.
- Phosphorus – energy production and photosynthesis
- Zinc – auxin production to drive rooting
- Boron – cell membrane integrity for strong, healthy roots
- Manganese – photosynthesis (responsible for splitting the H2O molecule)
- Biostimulants (Transit-S) – abiotic stress management, root growth, & improving nutrient use efficiency

Ensuring the soil is equipped with soil applied nutrients to support the seedling and drive rooting
- Zinc – auxin production to drive rooting
- Manganese – photosynthesis (responsible for splitting the H2O molecule)
- Biostimulants (Synergro M2) – drive rooting and nutrient use efficiency

During this next phase of rapid vegetative growth, the crop requires a huge amount of energy. Pairing these key nutrients with a herbicide application is the best way to meet the increased nutritional demand of the crop:
- Phosphorus – energy production
- Potassium & Magnesium – critical for carbohydrate movement for yield production
- Zinc – root and shoot differentiation and moisture acquisition
- Copper – lignification of cell walls for standability and disease management
- Boron – membrane integrity for strong, healthy roots.
- Biostimulants (Transit-S) – abiotic stress management, root growth, & improving nutrient use efficiency

As the crop moves to the reproductive stage, there are key nutrients essential for pollination and fertilization. Ensuring these nutrients are present in adequate amounts prior to pollination is key:
- Zinc – auxin production for pollen tube elongation
- Boron – pollination
- Calcium –
- Biostimulants (Cellburst) – pollen tube elongation

During later season ripening, this is the stage where nutrition can impact the quality of the cereal crop. Applying these nutrients later in the season can have a positive impact on protein content:
- Nitrogen – drive protein production
- Zinc – better seed vigor and germination for next year’s crop
Nutrient Uptake Calculator
Use our crop uptake and removal calculator to determine how much of each nutrient is required for your targeted yield.
System of Chemtrition
PreCede
+ Seed Protectant
Rate: 1.0L/MT Timing: Seed

- Drive lateral rooting with the optimal ratio of manganese and copper.
- Increase root development and eliminate carbohydrate root exudation with the addition of zinc and boron.
- Synergistic impact to rooting when combined with seed protection products to improve overall plant health.
ReLeaf
+ Herbicide
Rate: 1.0L/ac Timing: Foliar

- Improve nutrient uptake and drive rooting with proper ratio and forms of phosphorus.
- Manganese applied to balance phosphorus loading to drive rooting and photosynthesis.
- Increase lignin strength and photosynthetic efficiency with supplementary copper and zinc
42PHI
+ Fungicide
Rate: 0.5-1.0L/MT Timing: Foliar

- Increase nutrient uptake and synergy with fungicides with proper ratio and forms of phosphorus.
- Increase pollination with additional boron.
- Ensure the movement of carbohydrates and sugars to the reproductive parts of the plant by optimizing levels of potassium and magnesium
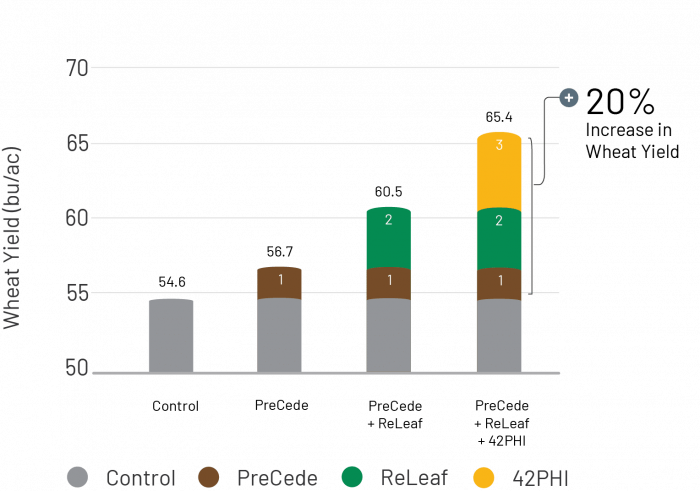
Proven Agronomic Performance
Field demo trials conducted in Western Canada proved the synergistic effects of the System of Chemtrition in Wheat, showing an average increase of 20% in Wheat yield.
BBCH
TIMING

Seed Treatment
Soil
Herbicide

Fungicide
Product Name
Rate L/ac
Analysis 3-15-7/ Zn
Product Name
Rate L/ac
Analysis 3-15-7/ Zn
Product Name
Rate L/ac
Analysis 3-15-7/ Zn
Product Name
Rate L/ac
Analysis 3-15-7/ Zn
Product Name
Rate L/ac
Analysis 3-15-7/ Zn
Related Articles

Alberta growers get 50% back on NutriScan with Alberta Farm Technology Program
Don’t miss out – Alberta growers get 50% back on NutriScan with Alberta Farm
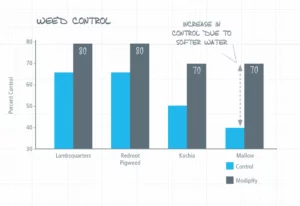
Hard water decreasing your herbicide efficacy?
May has arrived, and that means seeding is in full swing! As you head

Getting Started with a Soil Test
It all begins with a soil test! To maximize the genetic potential of your

8 Reasons to Soil Test
Soil testing is a best management practice (BMP) and a foundational step in preserving







